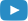
How to Dispose of Lithium-Ion Batteries Safely and Responsibly
Lithium-ion batteries have become an integral part of daily life, utilized in devices such as smartphones, laptops, electric vehicles, and large-scale energy storage systems. Their popularity stems from their ability to store significant amounts of energy, endure numerous charge cycles, and operate efficiently. These batteries are extensively employed in residential, commercial, and industrial settings. However, as the usage of lithium-ion batteries increases among individuals and organizations, the issue of improper disposal is escalating. Incorrect disposal of these batteries can lead to fires, leakage of hazardous substances, and environmental damage. It is now more critical than ever for all stakeholders—individuals, businesses, and manufacturers—to be informed about the proper disposal methods for lithium-ion batteries and to recognize the importance of responsible recycling.
Why Improper Disposal Is Dangerous?
When lithium-ion batteries reach the end of their service life, many users are unsure how to handle them. Some are stored indefinitely, while others are mistakenly thrown into household waste. This lack of awareness poses significant risks. Damaged or discarded lithium-ion batteries can overheat, short-circuit, or ignite, causing fires in landfills, waste facilities, or during transportation. Beyond safety concerns, these batteries contain valuable and hazardous materials that can contaminate soil and water if released uncontrolled.
The solution lies in proper disposal and recycling. By following approved recycling pathways, lithium-ion batteries can be safely processed, valuable materials can be recovered, and environmental harm can be significantly reduced.
How Should Lithium-Ion Batteries Be Disposed Of?
Lithium-ion batteries should never be disposed of in regular household or commercial waste. They must be collected and sent to certified battery recycling or hazardous waste facilities, where they are safely discharged, dismantled, and processed. Proper disposal prevents fire risks, ensures regulatory compliance, and enables the recovery of valuable materials such as lithium, cobalt, nickel, and copper.

What Are Lithium-Ion Batteries?
Lithium-ion batteries are rechargeable devices that store energy by moving lithium ions between the anode and cathode during charging and discharging. A standard lithium-ion battery includes four key parts: an anode (typically graphite), a cathode (generally a lithium metal oxide), a separator, and an electrolyte that enables ion movement. Compared to older battery types like lead-acid or nickel-metal hydride, lithium-ion batteries provide greater energy density, reduced self-discharge, and longer service life. These technical benefits have led to their broad use, but they also make managing the batteries at the end of their life more complicated and important.
What Are Lithium-Ion Batteries Used For?
Lithium-ion batteries are used across a broad range of applications. In consumer electronics, they power smartphones, laptops, tablets, cameras, and wearable devices. In transportation, they serve as the core energy source for electric vehicles, electric buses, and industrial mobility solutions. On a larger scale, lithium-ion batteries are integral to residential, commercial, and grid-scale energy storage systems, where they store electricity generated from renewable sources such as solar and wind power and release it during peak demand periods. Each of these applications generates battery waste at different scales, requiring tailored disposal and recycling strategies.
How Are Lithium-Ion Batteries Recycled?
To ensure both safety and sustainability, the recycling procedure for lithium-ion batteries follows a rigorous, step-by-step approach. The process is designed to optimize the reclamation of high-value materials through several essential stages: initial collection and sorting, followed by intensive mechanical processing and sophisticated recovery techniques.

Collection, Sorting, and Pre-Processing
Used lithium-ion batteries are collected through municipal recycling programs, manufacturer take-back schemes, industrial recovery channels, or specialized recycling partners. During collection, batteries must be handled carefully to avoid physical damage or short circuits. Once collected, batteries are sorted according to chemistry, size, and application, as different battery types require different processing methods.
Mechanical Crushing and Material Separation
Batteries are mechanically shredded or crushed in controlled settings following sorting. In order to separate metals, plastics, and active materials, this step disassembles battery packs into smaller parts. To separate particular material streams, technologies such as magnetic, air classification, and screening are employed.
Hydrometallurgical Processing and Black Mass Recovery
One of the most essential products derived from the recycling of lithium-ion batteries is known as "black mass"—a fine powder that encompasses valuable materials including lithium, cobalt, nickel, manganese, graphite, copper, and aluminum. Hydrometallurgical methods employ chemical solutions to dissolve and selectively extract these metals. The black mass acts as a crucial intermediate product that can be further processed and repurposed in the manufacturing of new batteries, thereby promoting a circular economy.
Pyrometallurgical Processing
In certain instances, pyrometallurgical techniques are utilized. These methods entail high-temperature smelting to isolate and reclaim metals. Although they are effective for specific types of batteries, this approach is typically more energy-consuming and is frequently integrated with other recycling methods to enhance overall efficiency.
Benefits of Recycling Lithium-Ion Batteries
Recycling lithium-ion batteries delivers significant environmental, economic, and social benefits. Environmentally, recycling prevents hazardous substances from entering ecosystems and reduces the volume of waste sent to landfills or incinerators. Economically, it enables the recovery of high-value materials, reducing reliance on mining and lowering raw material costs. Socially, responsible recycling reduces human exposure to toxic chemicals and supports safer waste management practices across communities.
While lithium-ion batteries are the backbone of the global energy transition, their value extends far beyond initial performance. As adoption scales, integrating sustainable lifecycle management and responsible end-of-life handling is no longer a choice—it is a necessity for a circular economy.
At the manufacturing level, sustainability begins with durability-first engineering. By prioritizing stable cell chemistry and extended cycle life, we significantly reduce replacement frequency and minimize electronic waste. As a leading lithium battery manufacturer, we provide high-efficiency energy storage solutions tailored for residential, commercial, and industrial sectors.
Consult with our experts: If you are evaluating battery specifications or need custom system design, reach out to us for detailed technical support and a transparent quote.



 Home
Home
 Global Energy Storage 2025: 5 Massive Shifts Reshaping the BESS Landscape
Global Energy Storage 2025: 5 Massive Shifts Reshaping the BESS Landscape 
 May 26,2025
May 26,2025 

 Address: Wanyang Gold and Silver Building 6, Circular Economy Park, Sili Town, Jiyuan City, Henan Province, China
Address: Wanyang Gold and Silver Building 6, Circular Economy Park, Sili Town, Jiyuan City, Henan Province, China